
If you want better search rankings, more traffic, and a smoother user experience, one of the best things you can do to achieve all three goals is perform a comprehensive SEO audit.
Doing this helps you identify the technical and on-page issues that are holding your website back, including…
- broken pages
- slow-loading content
- duplicate metadata
- missing schema
- problems with how your site is being crawled.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through how to run a full SEO site audit and spot all the above issues (and more!). By the end, you’ll not only have a clear picture of your site’s health — you’ll also know exactly what to fix to improve it.
Now, one thing I should mention is that performing a site audit requires an SEO tool. The one we use at Style Factory is called Semrush, and if you’d like to follow along with what I’m doing, you can grab an extended trial of this here.
If you’re using another tool, not to worry — the same basic principles apply and you should still be able to use the below steps to audit your website successfully.
1. Set up your SEO project
To get started with your SEO audit, start a Semrush trial or log into your account. Once you’ve done that, navigate to the SEO > SEO Dashboard section.
Click Create SEO Project, enter your domain, and give your project a name.
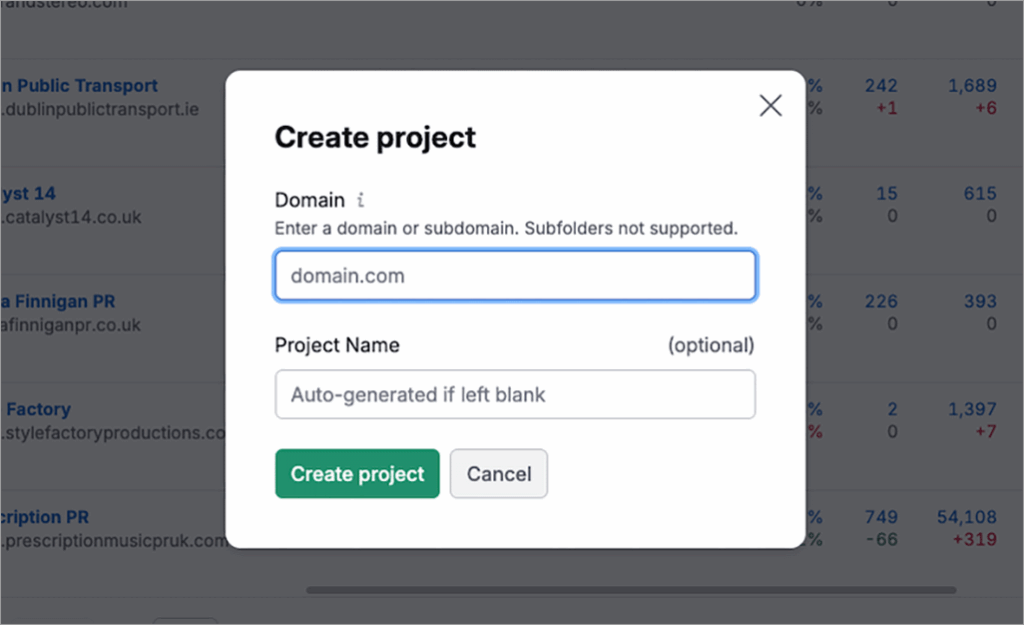
This creates a dedicated workspace for your website and unlocks access to all of Semrush’s project-based tools, including:
- Site Audit
- Position Tracking
- On Page SEO Checker
- Backlink Audit
- Organic Traffic Insights
2. Configure your site audit settings
Next, you’ve got to configure your site audit settings. In Semrush, go to the Site Audit section and click the ‘Set up’ button beside your project.
You’ll then be asked to configure your crawl settings. These include:
- Crawl scope: you can crawl your entire site for problems, or limit your audit to certain subdomains or subfolders on it.
- Pages to crawl: this lets you specify whether Semrush should crawl your site based on looking at internal links on your website, its sitemap, or a custom website URL list.
- Schedule: this lets you specify how often you’d like to crawl your site.
- Number of pages: this lets you tell Semrush how many pages to crawl (limits apply here, depending on your Semrush pricing plan).
- User-agent: this lets you choose whether Semrush should crawl as its own bot — SiteAuditBot — or impersonate Google’s, and whether you want to audit the desktop or mobile version of your site. In most cases, going for the SiteAuditBot option will give you the most detailed results — and when it comes to whether or not to crawl the desktop or mobile versions of your site, I would base this decision on which version of your site gets the most visitors.
- URL parameter rules: you can use this section to exclude any pages on your site that you don’t want crawled.
- Restrictions to bypass: this section lets you ignore any rules that you’ve put in your robots.txt file about crawling your site, or provide passwords to Semrush so that it can access protected areas of your site.
Once you’re happy with your settings, click Start Site Audit. You’ll see a progress bar while it runs.
3. Check your site’s health score
Once your crawl is complete, you’ll be taken to your site audit dashboard.
At the top of the screen, you’ll see a Site Health Score — a percentage score that reflects the overall technical health of your site. This is based on the number and severity of issues that Semrush has detected, and it lets you get an immediate sense of what shape your site is in.
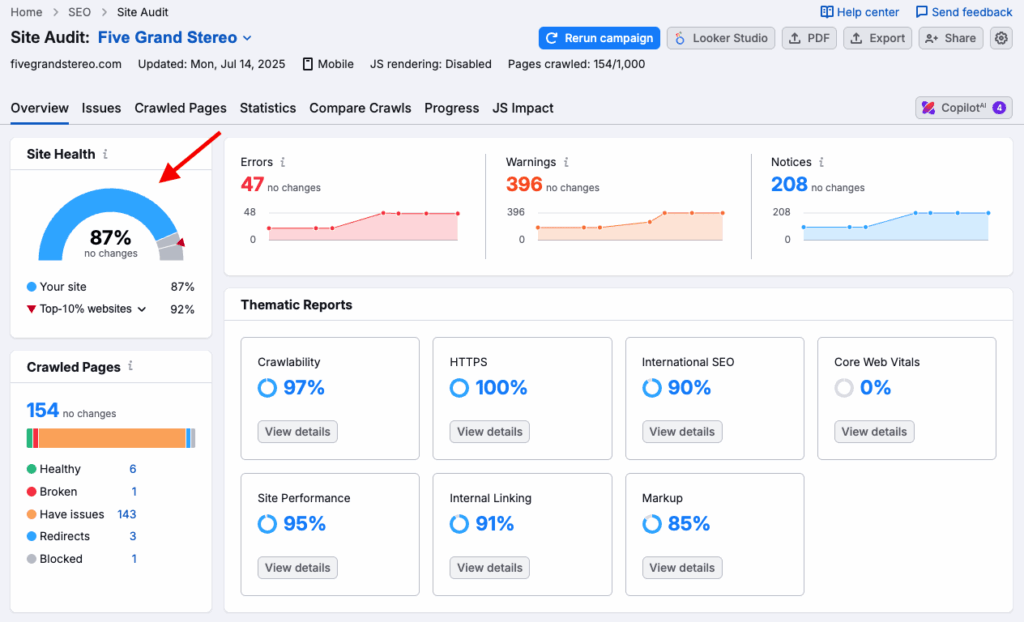
You’ll also get an at-a-glance overview of the volume of problems that Semrush has found (see my screenshot below).
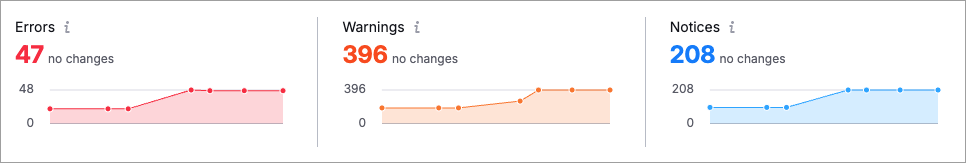
This is divided up into three categories:
- Errors: The most critical problems (for example, broken pages or missing page titles).
- Warnings: Medium-severity issues (e.g., slow load times, duplicate meta tags).
- Notices: Lower-priority suggestions (e.g., image alt attributes)
Now it’s time to work your way through the list of problems that Semrush has identified — with the ultimate aim of improving your site health score.
There are a few ways to do this, but a good way to go through things systematically is to use the ‘thematic reports’ that Semrush provides, starting with its crawlability one.

4. Fix crawlability and indexability issues
Crawlability and indexability are crucial to SEO: if search engines can’t find or access your pages, they simply won’t appear in search results.
Things that typically stop your site from being indexed properly include:
- Your robots.txt file instructing bots not to crawl certain pages.
- Pages being tagged as ‘noindex’ — this asks search engines not to include them in results.
- Broken internal links — i.e. links that point to URLs that no longer exist.
- Orphaned pages — pages that don’t have any internal links pointing to them.
- Slow server response times.
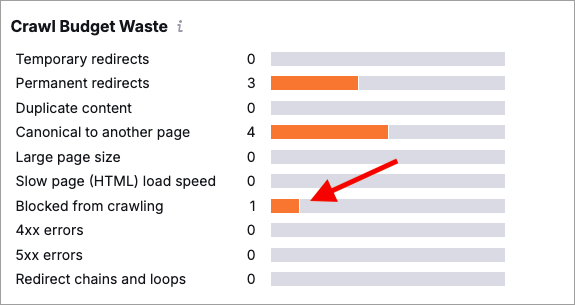
Going into the crawlability section in Semrush lets you see how many pages in your site are indexable — you can click on the ‘blocked from crawling’ statistic to get a list of all the pages that Google currently can’t access.
Now in many cases, blocked pages are actually a good thing. There are certain bits of your site — for example admin login pages, checkout pages, or search result pages — that you don’t really want Google to index.
But if you see any pages in Semrush’s ‘blocked from crawling’ box (pictured below) that you do want to see featured in search engine results, it’s worth investigating their technical configuration — you might find, for example, that you’ve added a noindex tag (which blocks content being crawled) to an important page by mistake.
Another key thing to pay attention to here is https status codes — 4xx errors typically indicate that the URL of a page is malformed or can’t be found, and 5xx errors crop up when your server can’t deliver a page on your site.
In a Semrush site audit, you can click on the relevant sections of the https status codes pie chart to see a list of problem pages, which you (or your developer) can then fix.
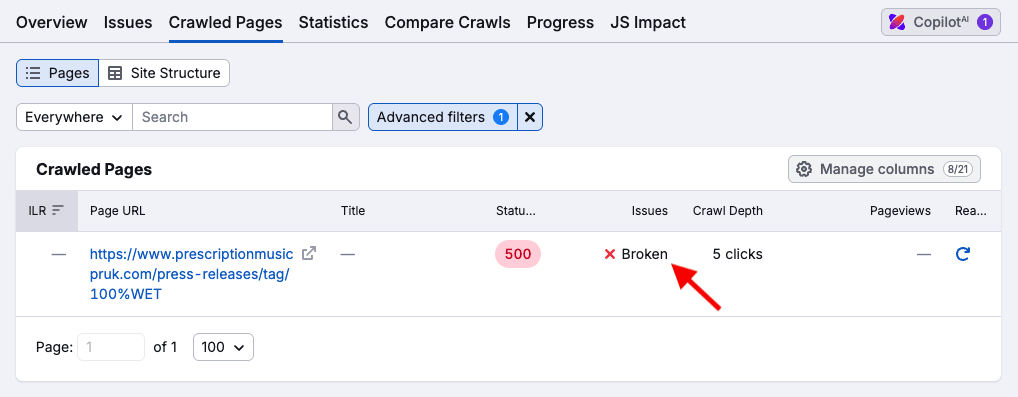
You might also want to spend a bit of time examining any page crawl depth issues highlighted by Semrush. Crawl depth refers to how many clicks away a page is from your website’s homepage — pages that are buried too deep in your site architecture can be harder for Google to find.
So, for example, if you’ve got an important piece of content on your site, but it’s four clicks away from your home page, you might want to consider linking to it from the home page, or from well linked-to pages on your website.
5. Inspect site security
Security is a key ranking factor, so it’s important to be aware of any vulnerabilities in your HTTPS implementation. To do this in Semrush, go back to your Site Audit overview and then click on ‘HTTPS’.
This will highlight any issues with your SSL certificate, server and website architecture.
Keep a particular eye out for issues relating to misconfigured SSL certificates. When someone visits your site, its SSL certificate ensures that anything they enter into it — like passwords, credit card details, or contact info — is scrambled into unreadable code while it travels over the internet.
So you spot any problems with your SSL certificates, consider these as urgent fixes.
6. Evaluate Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals (CWV) are a set of metrics created by Google that measure how fast, stable, and responsive your website feels to users. Sites that perform well on all three fronts can benefit from a ranking boost.
To see if you’re meeting Google’s expectations here, go to your Semrush site audit’s Core Web Vitals section, where you’ll find data on:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) — the time it takes for a browser to load the largest block of content on a page.
- Total Blocking time (TBT) — the time a page is unavailable for data input.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) — how much page ‘jumps around’ while loading.
You can then identify any areas for improvement. Note however that fixing Core Web Vitals issues can involve some fairly technical work on your website, so you may need to seek help from a developer to do so.
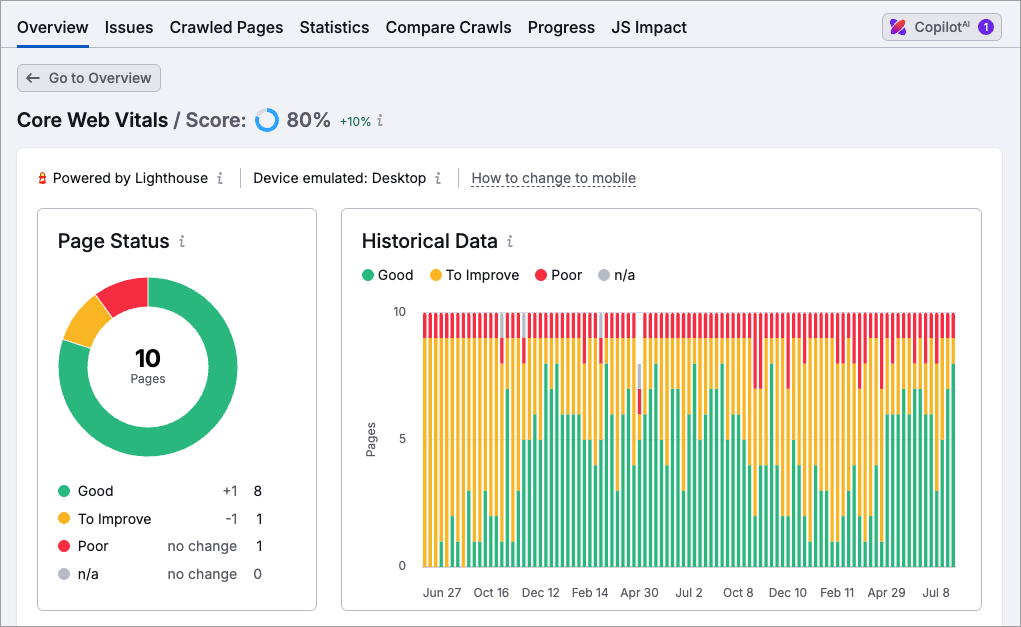
The other thing worth noting here is that Semrush uses ‘lab test’ information when evaluating Core Web Vitals scores, instead of real-world visitor data (‘field data’). If you want to see Core Web Vitals scores based on actual user data, it’s better to use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool or the Core Web Vitals section of the Google Search Console platform.
💡Tip: Generally speaking, it’s worth tackling more serious technical SEO problems before dealing with Core Web Vitals. Google is on record as saying that although Core Web Vitals metrics are not irrelevant, they’re “not as important as some people think.”
7. Improve site speed
Improving site speed not only boosts rankings but also enhances user experience — especially for mobile device users.
To identify any problems with site speed in Semrush, go to your site audit and then to the Site Performance section (see screenshot below).
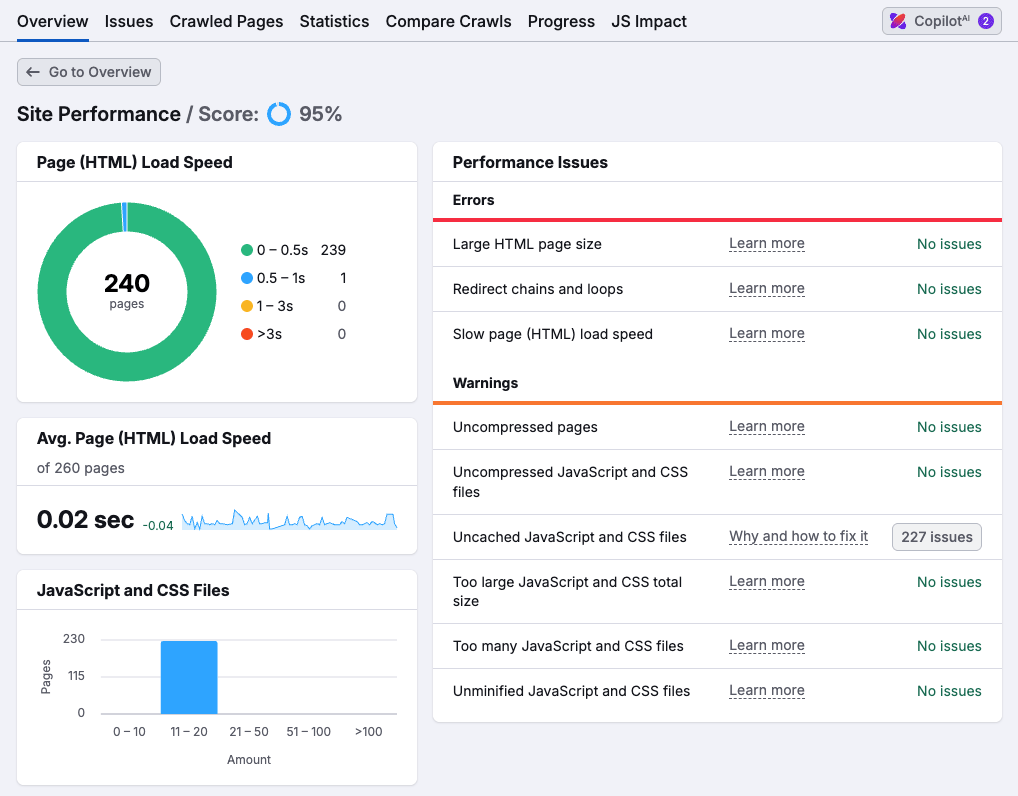
You’ll then be presented with a list of site issues that might be slowing your website down, for example:
- Large images or videos
- Uncompressed JavaScript and CSS
- Slow server response times
- Render-blocking resources
Fixing some of these problems should be straightforward enough — it’s easy enough to replace large images with smaller ones, or remove a third-party script that you don’t need any more, for example.
Addressing some issues may require technical skills however, and you may need some support from a developer with these.
8. Improve internal linking
Good internal linking helps both Google and users navigate your site more easily. And linking from authoritative pages — those with lots of external links pointing to them — to less authoritative ones can help your newer (or less popular) content perform better in search.
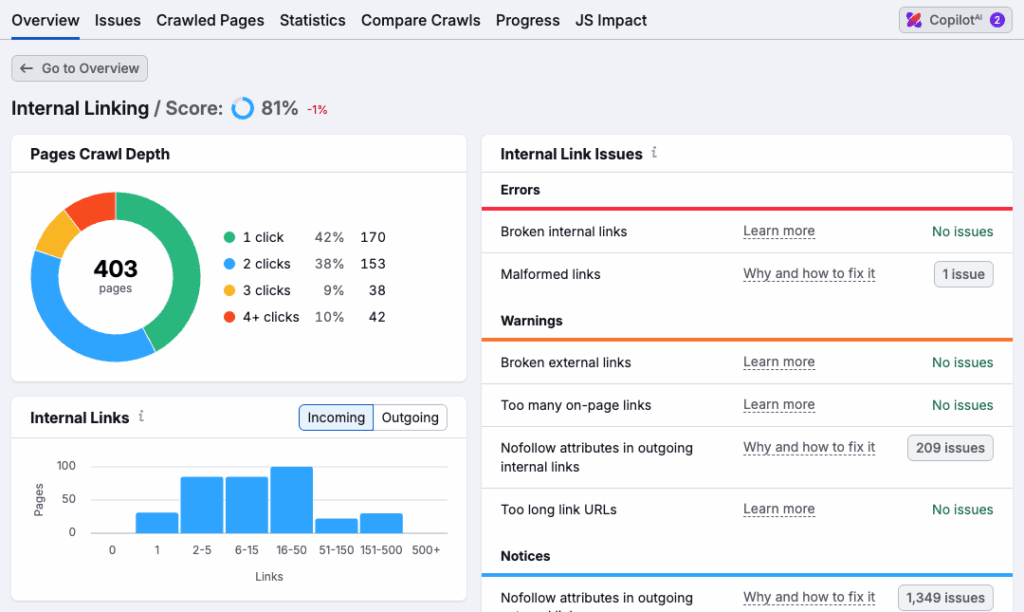
You can use the ‘Internal Linking’ report in your Semrush site audit (pictured in my screenshot above) to identify areas for improvement here. This highlights issues like:
- broken links
- orphaned pages that have no inbound links
- pages that are more than three clicks away from the homepage
- Overuse of nofollow attributes
- Missing anchor text
To fix these sort of problems, consider:
- adding breadcrumb navigation to your website
- using more contextual internal links within content
- building topic clusters to group related content.
Doing so can improve user experience, pass ‘link juice’ throughout your website more efficiently, and help search engines crawl your website more effectively.
9. Check Schema Markup implementation
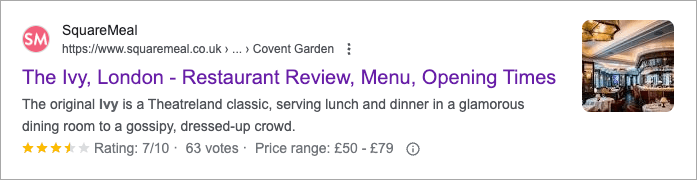
Schema markup is ‘structured data’ that you add to your website in order to give search engines more context about your content. For example, you can use Schema to tell Google that a page involves a recipe, a product, pricing information, a review etc.
Google will occasionally surface some of this information in its search results too in the form of ‘rich snippets’ — and these can sometimes encourage clickthroughs to your content.
It’s very easy to implement Schema incorrectly, however — so it’s worth checking in on the quality of your markup periodically. You can do this in a Semrush SEO site audit by navigating to the ‘Markup’ report and then looking for any instances of invalid structured data.

Once you’ve spotted these, you can correct any code errors.
10. Check page titles, headings and meta descriptions
Good page titles, headings and meta descriptions are key to helping search engines and users understand your content, and an SEO audit gives you the opportunity to check that you’re following best practice with regard to all three.
Page titles
Your page title, also known as the <title> tag, is the blue clickable link that users see in search results. And it’s one of the strongest on-page SEO signals.
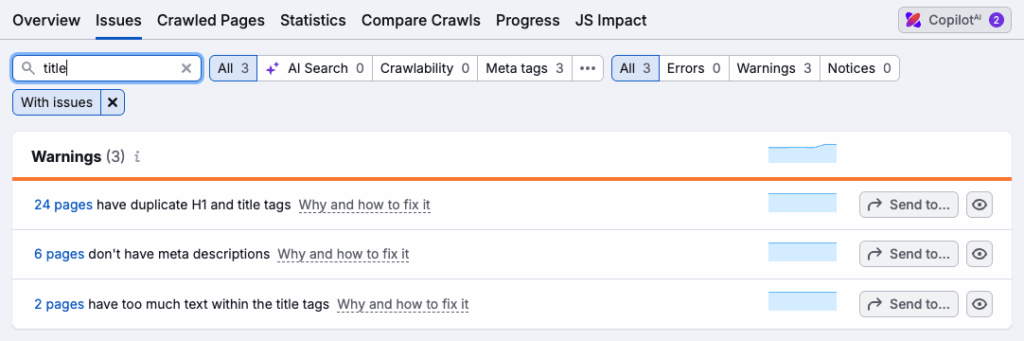
So, when auditing your site, check for:
- Missing title tags — pages without them won’t rank well.
- Duplicate title tags — these make it harder for search engines to surface the most relevant content.
- Title tags that are too long or short — if they’re too long, Google won’t be able to show the complete title, and if they’re too short, they won’t be providing enough context or keywords.
If using Semrush, you can identify any problems with title tags by going to your site audit report, clicking Issues, and then searching for ‘title’ (as per my screenshot below).
Headings
Headings help both users and search engines quickly understand the structure and topic of a page. The H1 heading tag signals the main theme of a page, while H2s, H3s and so on break it down into digestible sections.
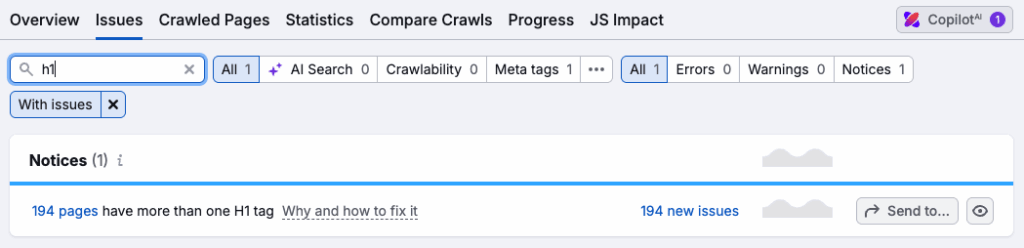
When auditing a site, check that…
- there are no missing H1 headings on your site
- your heading structures make sense — i.e, H3s follow H2s, H2s follow H1s, and so on (tip: the free Headings Map extension for Chrome is a good tool for checking these)
- your H1s and page titles are not exactly the same — you’re missing out on keyword targeting opportunities if your H1s are identical to your titles.
In Semrush, you can spot any H1 issues by going to your site audit, clicking Issues and then searching for H1. This will bring up a list of any errors or warnings relating to H1 headings.
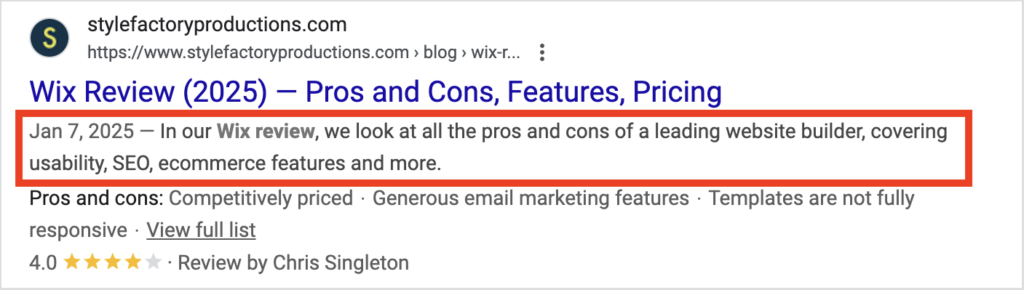
Meta descriptions
Meta descriptions are short pieces of text that summarize the content of a web page — you typically see them in search results, under page titles (see my screenshot below for an example).
Now, according to Google, meta descriptions don’t directly influence search rankings — but they can play a big role in how often people click on your links in search results. And this can have an indirect impact on rankings, because once somebody is on your site, it gives Google the opportunity to assess their interaction with it — with sites providing good user experiences and long dwell times potentially receiving preferential treatment in search results.
So, during a site audit, check for any missing meta descriptions, or overly long or short ones (aim to write them so that they are 150-160 characters in length).
In your Semrush site audit, you can spot any problems with your meta descriptions by going to the Issues tab and clicking the ‘Meta tags’ option.

11. Review content quality
Google insists that content quality is key to its performance in search results — it frequently talks about the importance of creating ‘helpful, reliable, people-first content.’
So, as part of an SEO audit, it’s worth looking beyond technical issues — and reviewing your content as part of your auditing process too. There is actually a set of questions provided by Google to help you do this, with some of the key ones being as follows:
- Does the content provide original information, reporting, research, or analysis?
- Does the content provide a substantial, complete, or comprehensive description of the topic?
- Does the content provide insightful analysis or interesting information that is beyond the obvious?
- If the content draws on other sources, does it avoid simply copying or rewriting those sources, and instead provide substantial additional value and originality?
- Does the main heading or page title provide a descriptive, helpful summary of the content
- Is this the sort of page you’d want to bookmark, share with a friend, or recommend?
- Would you expect to see this content in or referenced by a printed magazine, encyclopedia, or book?
You can also use Semrush to assess your content in various ways.
For example, you can use its SEO Writing Assistant feature to assess the quality of an existing page or post, and see recommended ways to improve it.
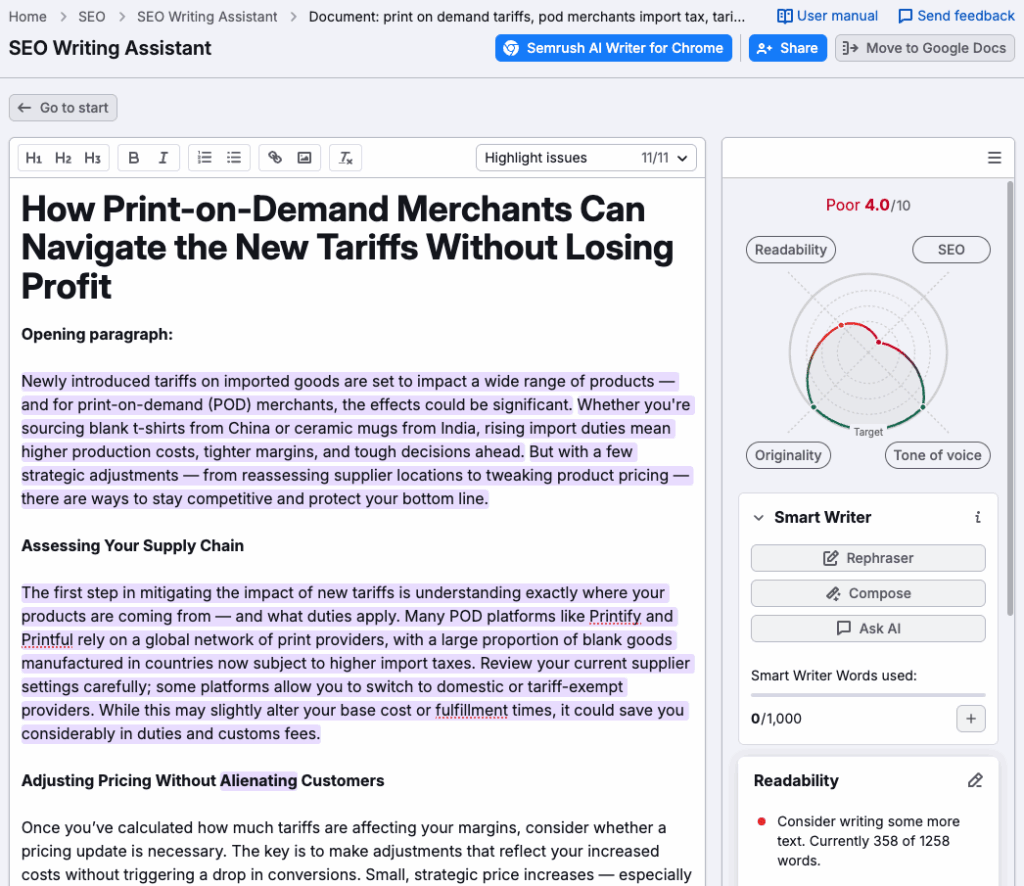
You can also use Semrush’s ‘On Page SEO’ Checker feature to get ideas for content improvement. Go its ‘Idea Tasks’ section and filter the results by ‘Content’ to see a list of things that Semrush thinks you can do to improve the quality of pages and posts on your website.
Another thing to audit your site for here is duplicate content — if you have any pages, posts or products that are extremely similar in nature, it may be worth consolidating them into one piece of content.
(Remember to create 301 redirects as appropriate if you do, though!).
12. Identify keyword opportunities
You might think of a site audit as a way to improve the state of your current content — but it’s also an opportunity to reflect on what content might be missing from your site.
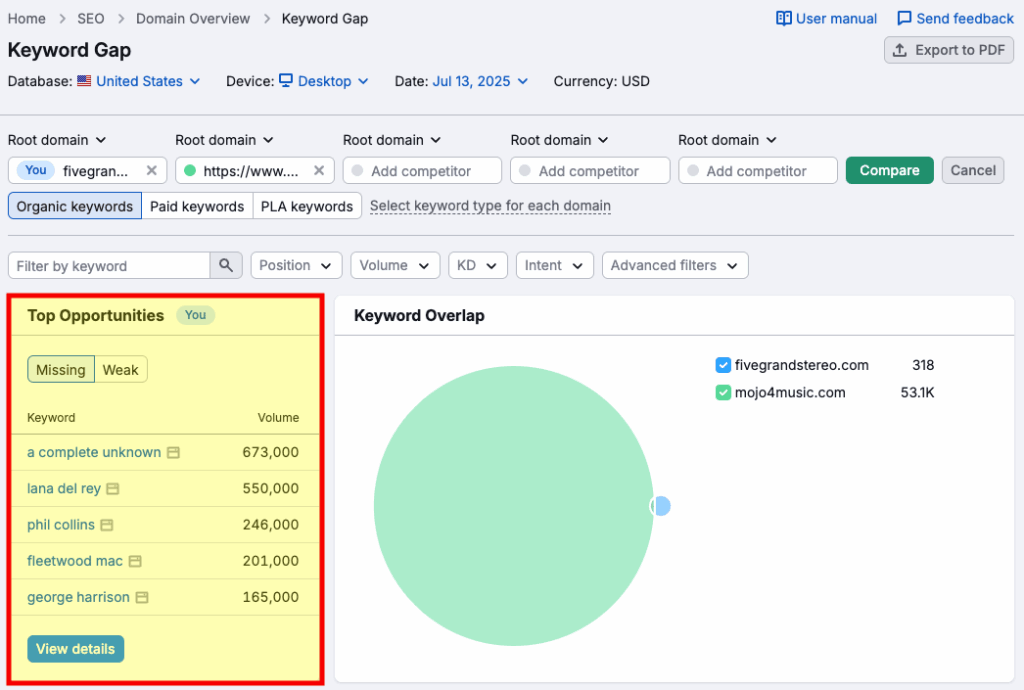
An easy way to get ideas for keyword targeting and content additions is by using Semrush’s ‘Keyword Gap’ feature. This lets you identify the keywords that your competitors are ranking for, but you’re not.
To use this, click on the Keyword Gap option under ‘Competitive Research’ in Semrush’s SEO section. Then, enter your domain along with up to three of your competitors. You’ll then be shown a list of opportunities that you might want to consider creating content for.
13. Identify backlink building opportunities
Backlinks are links to your website from other ones, and they’re a key part of SEO. This is because Google effectively views them as ‘votes’ for your content — the more high-quality sites that point to your site, the better the chance of your pages and posts ranking highly in search results.
If you’d like to identify link building opportunities for your website with Semrush, you can do this by navigating to its Link Building Tool, and then to your website project. You’ll then be presented with a list of ‘domain prospects’ — pages on websites that it’s worth trying to get links to your content from.

If you move one of these prospects into your ‘in progress’ pile, you’ll usually be able to access contact details for the editors of the websites in question.
14. Check your site structure
A well-organized site structure helps search engines crawl your site more efficiently, ensures that important pages are indexed, and makes it easier for users to navigate your content.
If your site is messy or disorganized — for example, if it contains buried pages, inconsistent internal links, or a confusing menu system — it’s going to cost you both traffic and conversions.
So as part of your SEO audit, review your website’s navigation and ensure that it is easy to use and foregrounds the most relevant content on your site. This will help your users get at your most important content, while giving search engines key context on the topics it should associate your website with.
15. Monitor progress through scheduled SEO audits and rank tracking
To maintain the SEO health of your site in the long term, you need to monitor its condition regularly, and ideally fix problems as soon as they crop up.
A key way to do this is to ensure that you’ve registered your site with Google Search Console. This free tool from Google lets you inspect your site regularly for any problems, and alerts you automatically via email to any issues it finds with your website.
You can also ensure that you’re monitoring progress effectively by using Semrush’s audit scheduling feature. Just go to your site audit’s settings in Semrush, and use the scheduling option to run site audits automatically on a regular basis.
Another way to sense-check whether your site’s technical setup or content needs attention is by tracking the positions of your pages and post in search results. A big drop in their visibility can indicate a problem with your site.
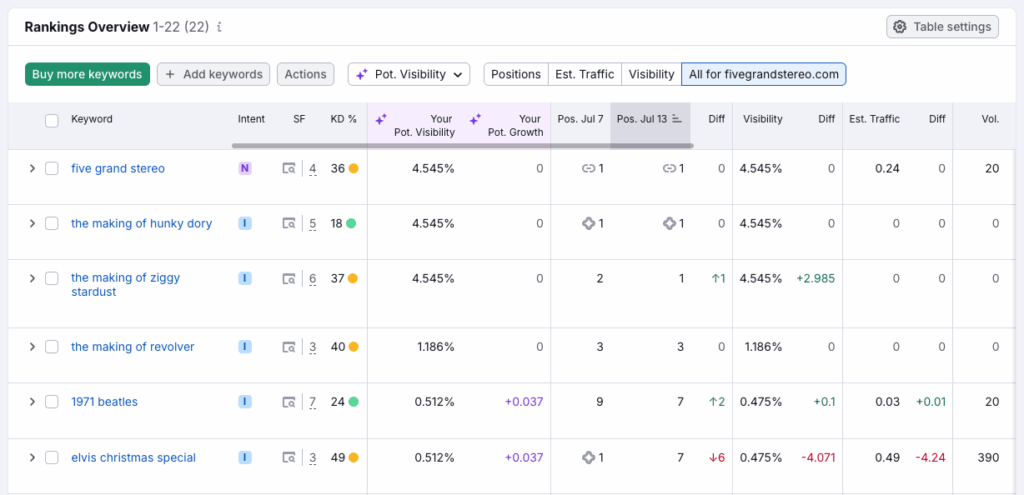
To set up position tracking in Semrush, go to its SEO section and then to Position Tracking. You’ll then be able to add the target keywords you want to track the rankings for and get daily or weekly reports on their performance.
If you notice an overall deterioration in these search positions at any point, that’s a big clue that it’s time to make significant improvements to your site’s SEO setup.
And of course, Google Analytics is your friend when it comes to monitoring SEO performance — you can use this to keep tabs on site traffic. As with rank tracking, if you spot any volatility (especially downturns in traffic), this is a big clue that there are SEO issues that need to be addressed.
Wrapping up
I hope you’ve found my SEO audit checklist useful! As discussed above, the key thing to remember is that SEO is an ongoing process, so make sure that once you start auditing your site, you make it a regular part of your workflow.
And on a related note, if you’d like ongoing (and free!) help with SEO, do sign up to our mailing list below — we regularly share useful tips on how to improve your Google rankings.
Don’t miss out on our free SEO toolkit
For a limited time only we’re offering our readers some excellent free SEO tools and resources. Sign up now to immediately receive:
- our downloadable cheatsheet containing the 20 key steps to ranking highly in search results
- extended free trials and discounts for leading SEO tools
- our downloadable cheatsheet on how to grow organic traffic to a blog
- 2 in-depth guides to SEO
- ongoing free tips and advice on SEO and growing your business
No comments